“Of course, business, just as life, is never a smooth curve. Failure can come as quickly, and more unexpectedly, as success. But true success is management of failure. Every time you hit a bad patch you must be able turn your fortunes around. That’s why it’s important to be always prepared for failure and build strong teams. To be a successful entrepreneur, venture capitalist or philanthropist, you must bring together people who know there will be problems, love to solve problems, and can work well as a team.” … “It reminds me not to be too proud. I celebrate failure — it can temper your character and pave the way for great achievement.” Kamran Elahian.
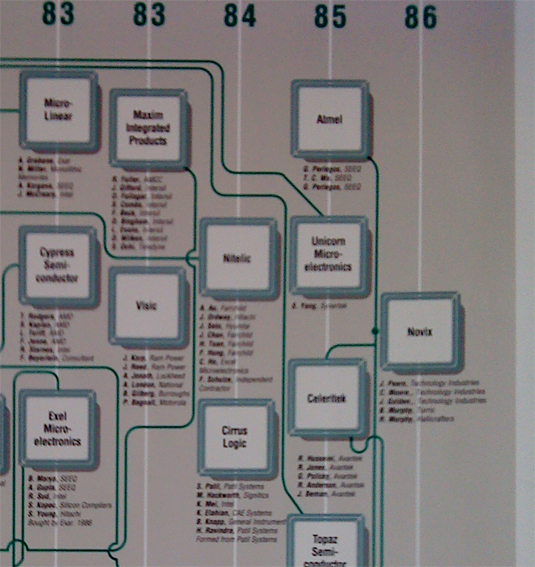
Kamran Elahian is a famous Silicon Valley entrepreneur. He was the founder of Cirrus Logic which is famous enough to be in the Silicon Valley Genealogy poster. The extract below lists the founders of the company, you can not read their names but they were 5 and here what the poster says: Suhal Patil (Patil Systems), Michael Hackworth (Signetics), Bill Knapp (General Instruments), M. Kei (Intel), H. Ravindra (Patil Systems) and Elahian himself (CAE Systems). Strangely, Elahian has a different list on his website — Suhas Patil, H. Ravindra, Bill Knapp, Mark Singer.
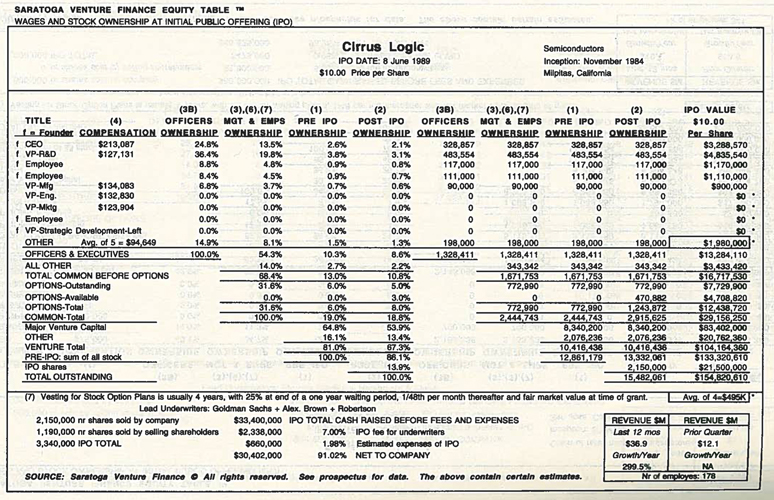
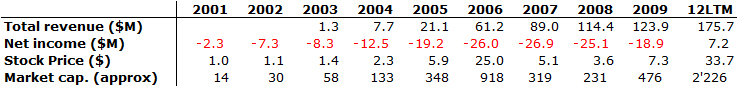
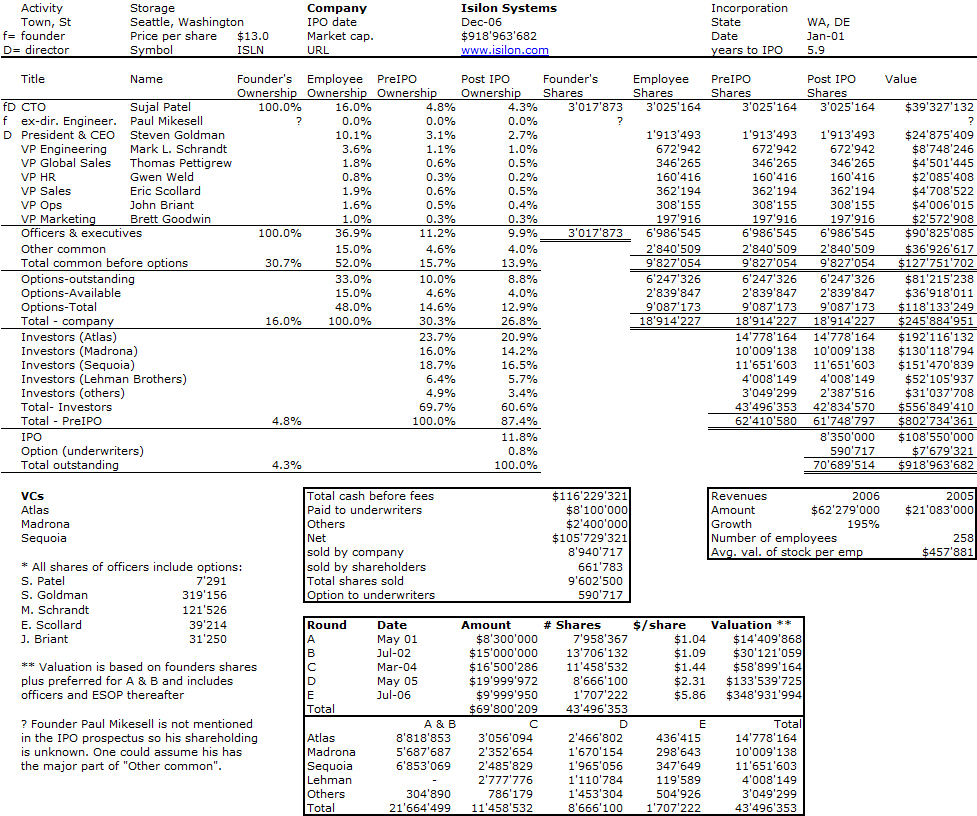
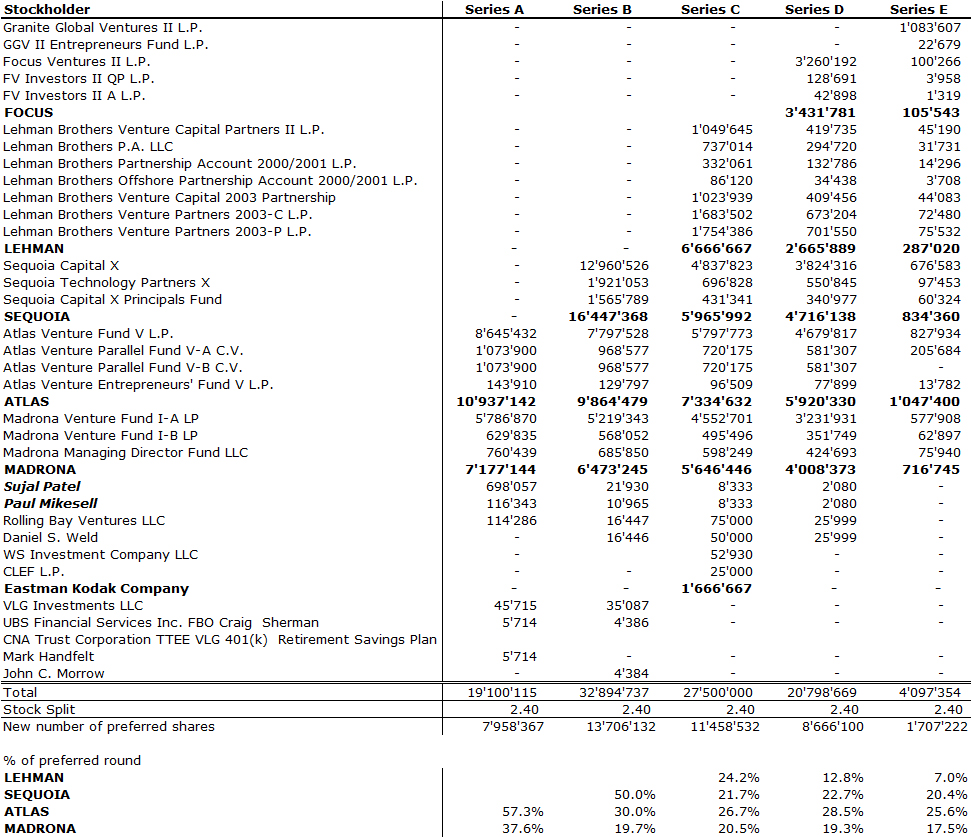
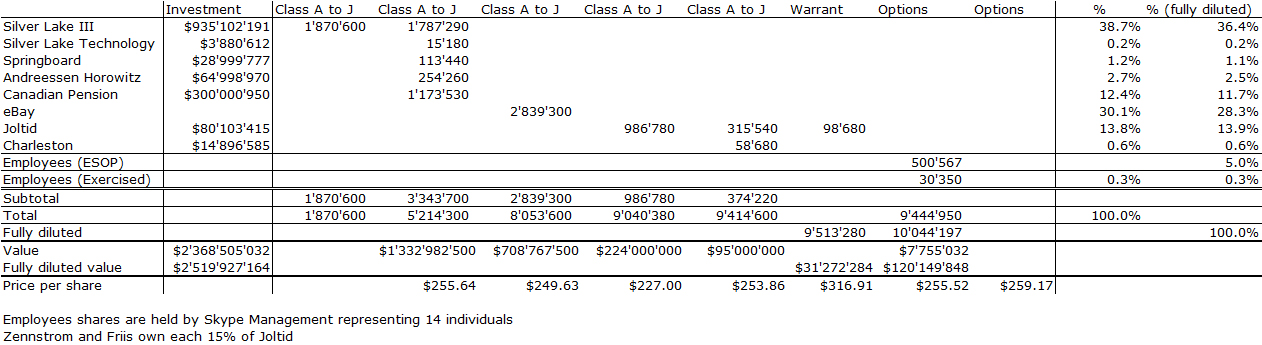
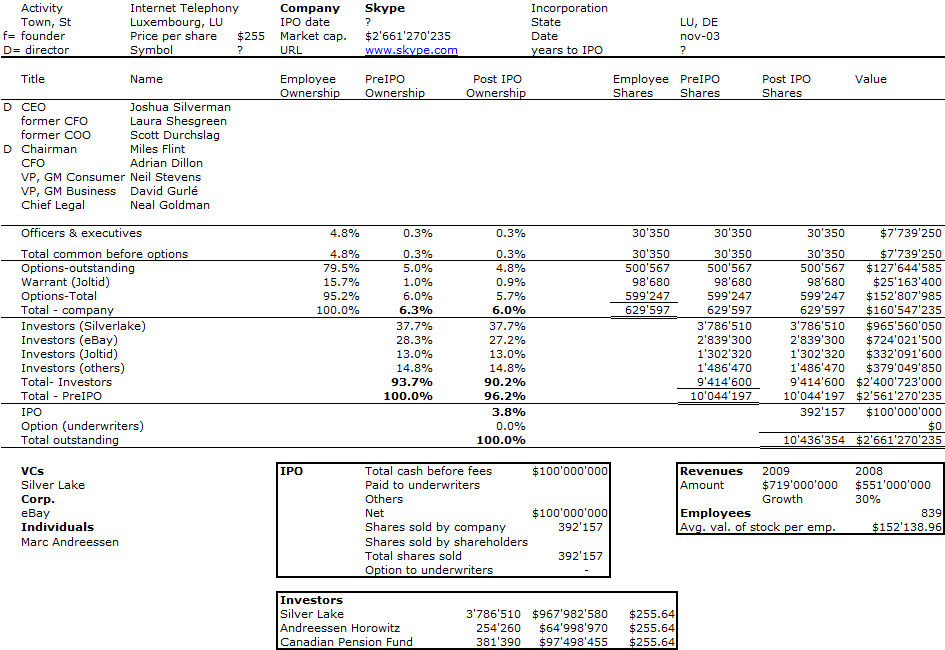
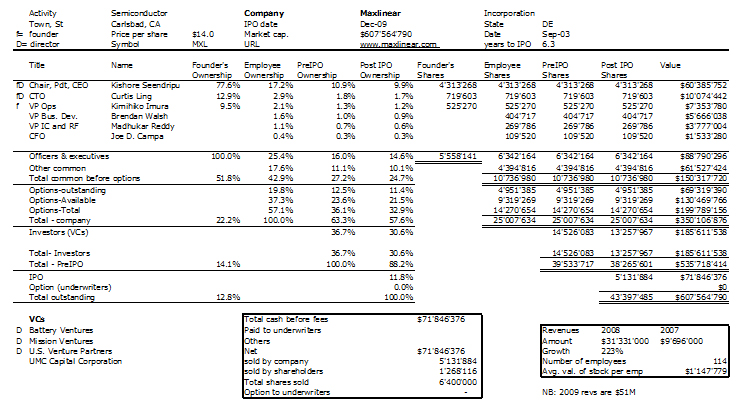
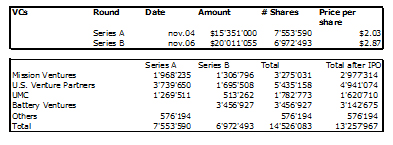
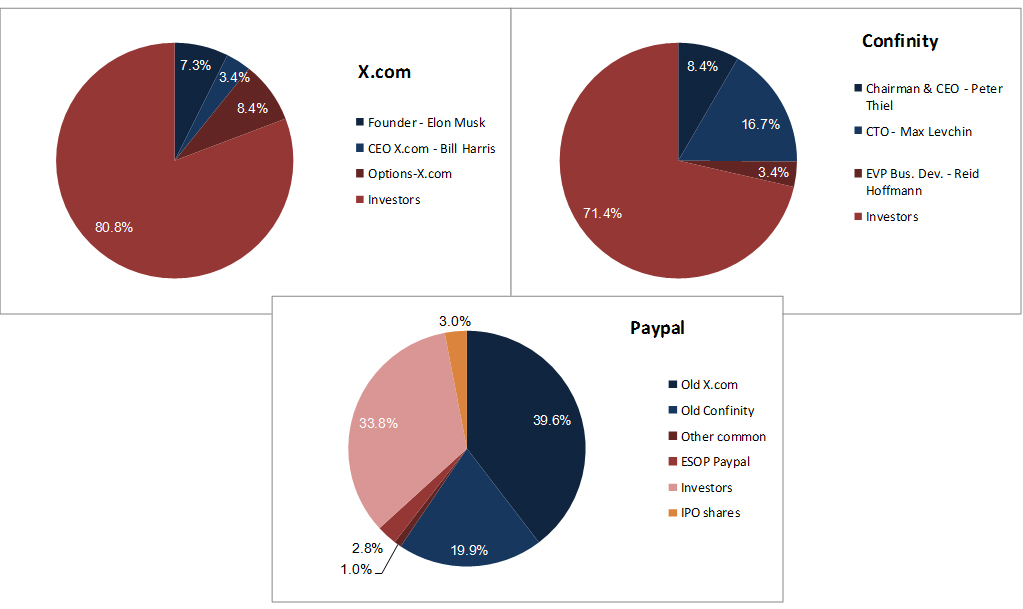
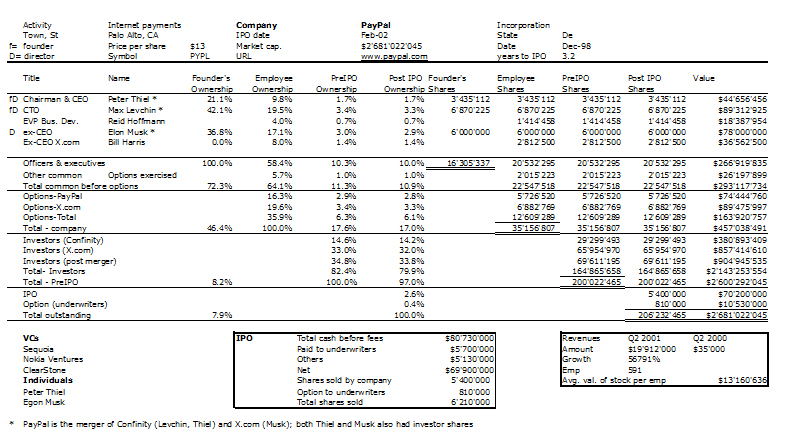
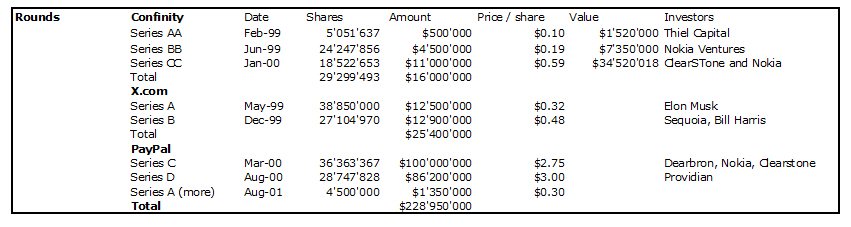
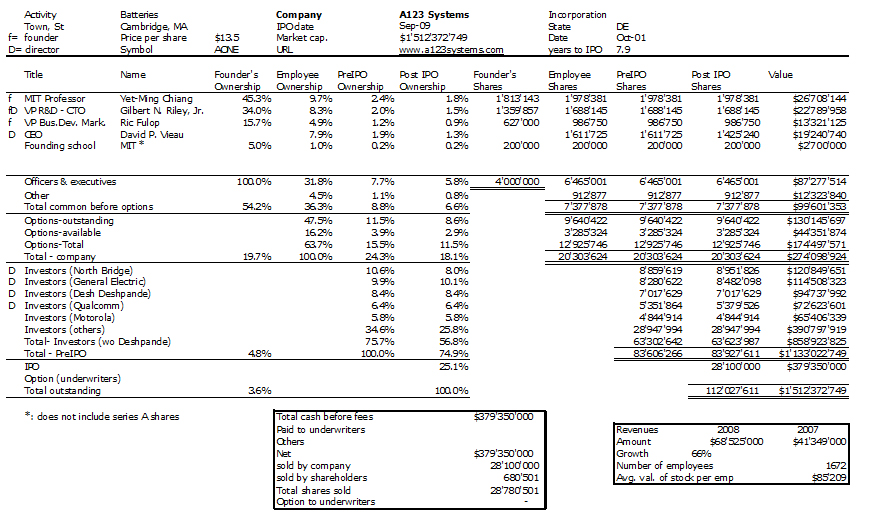
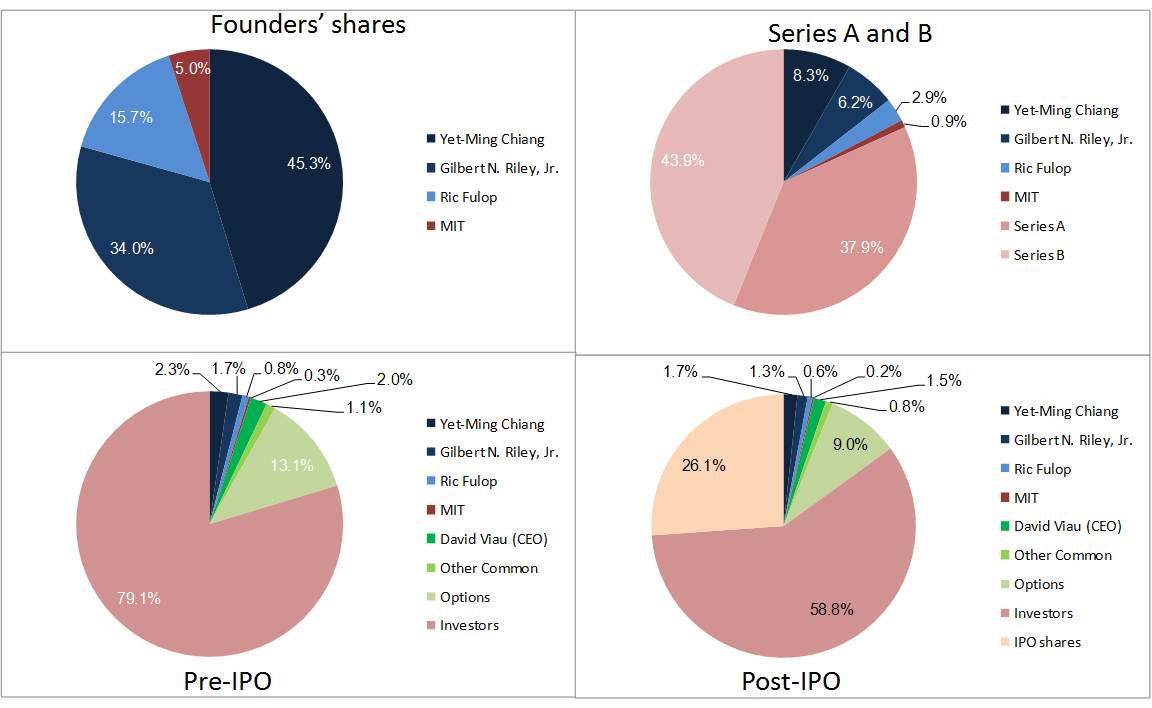
Nesheim in his book High Tech Start Up also mentions Cirrus as a success story and gives the cap. table at IPO. It is indeed his model I follow for my own cap. tables.
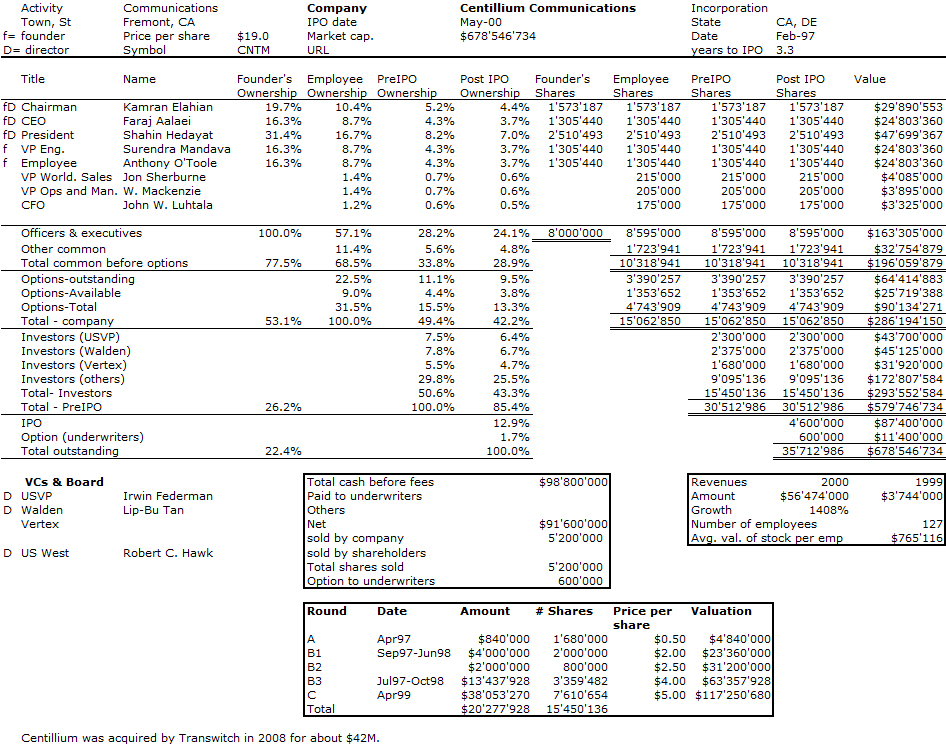
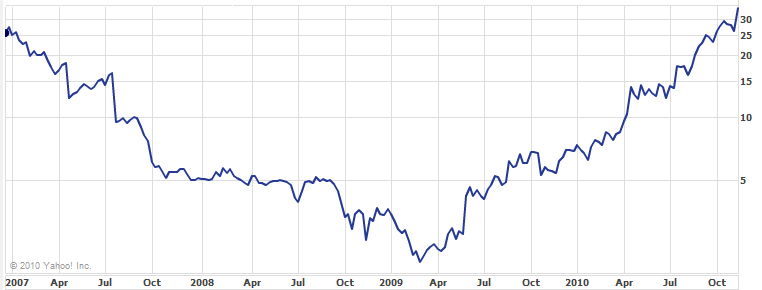
Then Elahian founded Centillium which unfortunately did not have the same end though its IPO was a great success. In 2008, the company was acquired for about $42M. So failure is followed by success and by failure again. Elahian also gives Centillium founders on his site: Shahin Hedayat, Faraj Aalaie, Babu Mandeva, Tony O’Toole.
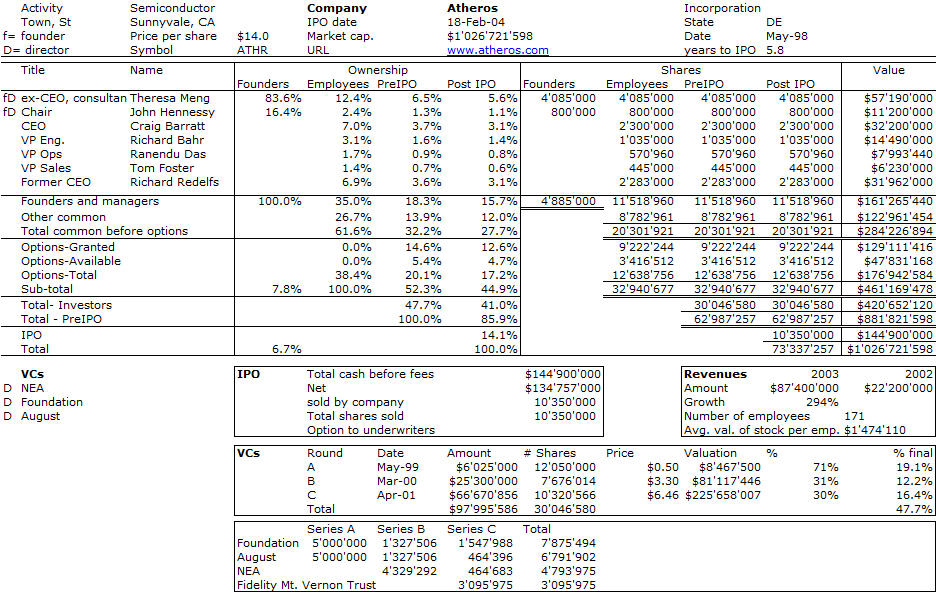
In the same area of chips, semiconductor for telecommunications, there is a similar story: Atheros has just annouced it would be acquired by Qualcomm for about $3.1B. Atheros is a company I had studied in my book because its two founders are two Stanford professors (Theresa Meng and John Hennessy, currently Stanford president) and its CEO is Craig Barratt whom I had as a teaching assistant when I was studying in California. Who says scientists/engineers cannot be great business people?!!
But the (possible) interest of all this is that you can compare three stories, more than 20 years apart and you cann see that there are tons of similarities and the web2.0 start-ups I covered recently are not so different.