Winning Opportunities is not just another book about business planning. Indeed Raphael Cohen’s new book is subtitled Proven Tools for Converting Your Projects into Success (without a Business Plan).
This 200-page, 18-(short)-chapter book is a very interesting way to analyze your project opportunity (maybe more in a corporate than in a start-up set-up). “Designed for doers, it provides a structured model of the entrepreneurial/intrapreneurial process. […], it is about discipline and process. […]. In other words, creativity is not enough. Framework and discipline are essential companions.” [Page 3] Cohen is therefore a disciple of Peter Drucker who believes entrepreneurs can be tought. But he adds on page 15, that “Observation is a state of mind. To understand your customers, you need to spend time observing them in their own environment. […]. There is no way engineers ensconced in their cubicle offices could observe (and so identify) such a “Pain”. Many real opportunities can only be identified outside of your office.” He is also close to Steve Blank and his customer development framework and here I should remind the reader with Blank’s comment on creativity.” But it’s more likely that until we truly understand how to teach creativity, [entrepreneurs] numbers are limited. Not everyone is an artist, after all.” And we should be all aware that though tools and states of mind are critical, success can not be guaranteed, its odds can increased however.
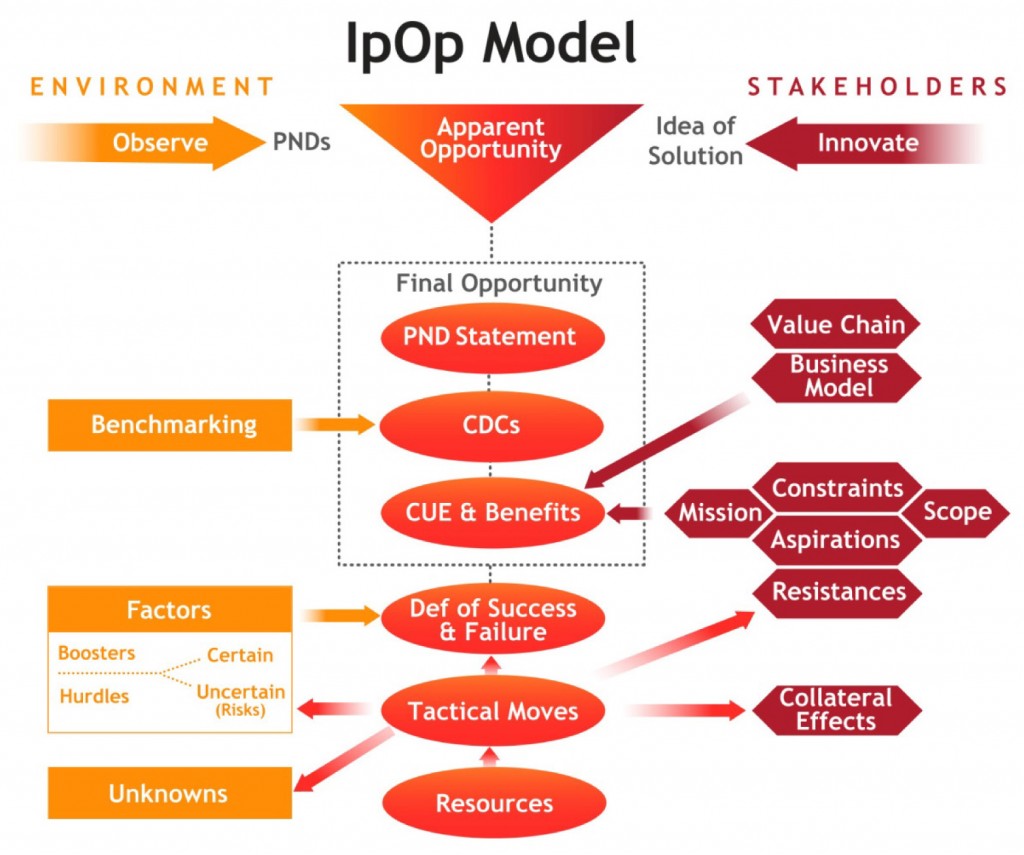
Cohen has a great framework that is summarized in the next figure but you should read his book and see how he builds the full IpOp (Innovation by Opportunity) model, step by step.
Again he is close to Blank when he explains that assumptions will be checked via practice, not via theory: “Selecting a Business Model usually requires making a number of assumptions. In many cases, it is impossible to verify these assumptions before implementing the Business Model in real time or at least in a pilot study. You should test a Business Model whenever possible, and must always be prepared to revise it or explore alternatives.” [Page 73]
One critical factor that may not be enough emphasized in business planning is the energy required to sell. “To be successful, it is not enough to have written up the perfect Business Model, you still need to persuade customers to buy. And for this, you must convince them that what you offer has an outstanding superior perceived value”. [Page 80]. You need to desire and be able to sell!
Cohen mentions metrics as a way to measure success. His KISS are Key Indicators of Success and these may be subjective. He is right. But once you decide about how you define success, measure it. “The Definition of Success determines a project’s sex appeal. […] While other factors such as preventing the competition from entering the market, testing new markets or distracting stakeholders from other issues may play a role in the decision process, it is the Definition of Success that is the bottom line. Whatever is measurable will always be very much at the heart of the decision process, because it is an output that can be monitored.” [Page 91] “Defining failure will provide stop/no stop criteria” [Page 92]. My personal experience is that it is one of the toughest decisions to admit one’s own failure. “If the opportunity is worth it, you will find the necessary resources when the time comes.” [Page 99].
Cohen introduces the concept of Unknowns as a separate chapter, showing again that entrepreneurship is not easy. They should be catalogued, characterized, prioritized. “Be humble enough to recognize what you do not know” [page 109] and “testing assumptions is often the key to reducing the level of uncertainty” [page 110]. One of the best examples of reducing unknowns is Arnaud Bertrand’s amazing testing with Housetrip.
Again entrepreneurship is about selling, making money, it is about action. “The fun part is in the action. This is why people excel at thinking of Tactical Moves. In fact, most people jump straight from identification of the Opportunity into planning Tactical Moves. Some even jump into the action without any planning at all. Because most creative people are action-oriented, their natural inclination is to skip the strategic analysis presented in the previous chapters. […] And these people like action” [Page 113] and again: “Finding Tactical Moves is a highly creative process” [Page 115].
At the same time, action can be scary, because of the possible collateral effects: “damaging the company’s reputation; altering the essence or image of an existing brand; upsetting distributors or other partners; reducing the market share of other company products (this is known as cannibalization); irritating management; disclosing critical information; making colleagues jealous” [Page 118]. I remember an entrepreneur from my Index days telling me, “each day, you take 10 decisions, 5 might be good, 5 might be bad; just hope the bad ones will not be deadly”. Action, Action!
“Contrary to common belief, entrepreneurs do not like to take risks” [Page 126] “What they like is success and they are willing to take risks to achieve it.” {…] “Managing risks means not only identifying them and anticipating their impact but also preparing contingency plans.” (cf Plan B by Mullins and Komisar, next blog paper or the famous Pivot by Blank / Ries). “The contingency plan sometimes turns out to be the main plan”. And it may mean rethink the Definition of Success and revisit the stop / no stop criteria. Once again uncertainty is highly present and decisions never black and white.
“Lack of money is often presented as the main obstacle to start-ups and intraprises. While this may sometimes be the case, the truth generally is that really attractive projects get the necessary funding. Of course, some people are more skilled than others in obtaining the Resources they need. Necessary qualities of an attractive entrepreneurial or intrapreneurial project are:
• The ability to deliver a convincing Definition of Success (plus possible additional Benefits) as against the Resources required (Return on Investment)
• A reasonable chance of success, given the team behind the project and other critical success Factors and Unknowns.
Many entrepreneurs are not lucid enough to make a realistic assessment of the attractiveness of their project, having a tendency to believe that what is attractive to them is automatically attractive to others. It is important that entrepreneurs seek resources from the right people. To do so, they will need a sufficiently large network to turn to.” [Pages 135-136]
“Fund-raising exacts an enormous collateral cost. The whole time spent on looking for money and convincing fund providers is unavailable to promoting delivery of the Definition of Success. The milestone-based is much healthier than putting a lot of energy into multiple rounds of financing, but is only possible with a very well-thought-out pre-project.” [Page 138]
Business plans are in fact more trouble than they are worth [page 151], because:
• They do not increase the probability of success of a new venture, […]
• Less than 10% of business plans actually get read. […]
• Production of the plan delays presentation of the project to Decision-makers
• Apart from people who make a living producing, teaching or selling business plans, almost everybody else in the business community agrees that they are useless for start-ups and new initiatives. The business plan does however remain relevant as the output of a strategic analysis for coordinating the functions of an existing organization (marketing, production, HR, finance, etc.)
• So … writing them is a waste of time and energy
Cohen finishes his book by explaining how important is an ecosystem friendly to entrepreneurs. “The simple Five P’s formula for emPowerment is a recipe that works wonders to promote innovation within organizations:
+ A Passionate leader
+ Permission (to do)
+ Protection (in the event of failure)
+ a Process
= Powerful Performance (by emPowered People)” [Page 185]
The book is extremely well-written and this is not so common in the business litterature. Another original feature is that Cohen does not use quotes (mea culpa!) at the beginning of each chapter but jokes. And because he authorizes the use of them, here is one I liked:
Making a compelling proposition pays
A guy with a severe stutter applied for a job selling Bibles. The interviewer believed he’d never make it as a salesman, and was about to tell the guy to look elsewhere for work. The stutterer begged for the job, “P-p-p-p-p-le-ease g-gg-g-ive m-m-m-mee a ch-ch-cha-a-ance. I-i-ic-c-can d-d-d-o i-i-tt.”
The manager said, “Okay”, and gave him a few Bibles and the rest of the day to see if he could sell one or two. By lunchtime, the stutterer was back, having sold all the Bibles. The manager was impressed, and asked if he could accompany the stutterer after lunch. “S-s-sure,” said the guy, and later they went out to the streets.
They approached a house, and the stutterer went up and knocked on the door. When the homeowner answered, he said, “G-g-g-g-good a-a-a-ftern-n-n-noon, M-m-ma’am. I-i-i’m s-s-s-selling B-b-b-bibles. W-w-w-w-would y-y-y-you l-l-l-l-l-like to b-b-b-buy a B-b-b-b-bible, or sh-sh-sh-ould I j-j-j-j-ust r-r-read it t-t-t-to you?”
A non-negligeable advantage of Cohen’s book is that it is freely downloadable and the author is just aksing you to pay what you think is fair once you’ve read it. I have not paid anything yet but my contribution has been to write this blog article and I would certainly recommend interested people to read and pay! Is this enough Raphael? 🙂