It seems global warming is around. But there are creative people like Candide Thovex who offer their own solutions. Very different from my 2010 post but enjoy the holidays!
Monthly Archives: December 2015
The business of biotech – Part 3: Genentech
I should have begun with Genentech this series of posts about Biotech (see part 1: Amgen or part 2 about more general stats). Genentech was not the first biotech start-up, it was Cetus, but Genentech was really the one which launched and defined this industry. All this really began with the Cohen Boyer collaboration. Genentech would have loved to get an exclusive license on their patent about recombinant DNA, but the universities could not agree for business as well as political reasons. Genentech was an unknown little start-up and genetic engineering a very sensitive topic at the time. Swanson had tried even to offer shares to Stanford and UCSF (the equivalent of 5% of the existing shares at the time).
Please note I already wrote about Genentech here in Bob Swanson & Herbert Boyer: Genentech. But this new post follows my reading of Genentech – The Beginnings of Biotech by Sally Smith Hughes.
Chronology
– November 1972 – Meeting of Cohen and Boyer at aconference in Hawaii
– March 1973: First joint lab. experiments
– November 1973: Scientific publication
– November 4, 1974: Patent filing
– May 1975: Cohen becomes an advisor for Cetus
– January 1976: Meeting between Swanson and Boyer
– April 7, 1976: Genentech foundation
– August 1878: first insulin produced
– Q2 1979: 4 research projects with Hoffmann – La Roche (interferon), Monsanto (animal growth hormone), Institut Mérieux (hepatitis B vaccine) and an internal one (thymosin).
– July 1979: first human growth hormone
– October 1982: FDA approval of Genentech insulin produced
– October 1985: FDA approval of human growth hormone
I have to admit I had never heard of the Bancroft Library’s website (http://bancroft.berkeley.edu/ROHO/projects/biosci) for the Program in Bioscience and Biotechnology Studies, “which centerpiece is a continually expanding oral history collection on bioscience and biotechnology [with ] in-depth, fully searchable interviews with basic biological scientists from numerous disciplines; with scientists, executives, attorneys, and others from the biotechnology industry.”
The invention of new research and business practices over a very short period
Swanson was captivated: “This idea [of genetic engineering] is absolutely fantastic; it is revolutionary; it will change the world; it’s the most important thing I have ever heard.” [… But Swanson was nearly alone.] “Cetus was not alone in its hesitation regarding the industrial application of recombinant DNA technology. Pharmaceutical and chemical corporations, conservative institutions at heart, also had reservations.” [Page 32] “Whatever practical applications I could see for recombinant DNA… were five to ten years away, and, therefore, there was no rush to get started, from a scientific point of view.” [Page 32] “I always maintain” Boyer reminisced, “that the best attribute we had was our naïveté… I think if we had known about all the problems we were going to encounter, we would have thought twice about starting… Naïveté was the extra added ingredient in biotechnology.” [Page 36]
The book shows the importance of scientific collaborations. Not just Boyer at UCSF but for example with a hospital in Los Angeles. A license was signed with City of Hope Hospital with a 2% royalty on sales on products based on the licensed technology. “[…] negotiated an agreement between Genentech and City of Hope that gave Genentech exclusive ownership of any and all patents based on the work and paid the medical center a 2 percent royalty on sales of products arising from the research.” [Page 57]
Even if in 2000, City of Hope had received $285M in royalties, it was not happy with the outcome. After many trials, the California Supreme Court in 2008 awarded another $300M to City of Hope. So the book shows that these collaborations gave also much legal litigation. [Page 58]
In a few years, Genentech could synthesize somatostatin, insulin, human growth hormone and interferon. It is fascinating to read how intense, uncertain, stressful these years were for Swanson, Perkins, Boyer and the small group of Genentech employees and academic partners (Goeddel, Kleid, Heyneker, Seeburg, Riggs, Itakura, Crea), in part because of the emerging competition from other start-ups (Biogen, Chiron) and academic labs (Harvard, UCSF).
“On August 25, 1978 – four days after Goeddel’s insulin chain-joining feat – the two parties signed a multimillion-dollar, twenty-year research and development agreement. For an upfront licensing fee of $500,000, Lilly got what it wanted: exclusive worldwide rights to manufacture and market human insulin using Genentech’s technology. Genentech was to receive 6 percent royalties and City of Hope 2 percent royalties on product sales.” [Page 94] They managed to negotiate a contractual condition limiting Lilly’s use of Genentech’s engineered bacteria to the manufacture of recombinant insulin alone. The technology would remain Genentech’s property, or so they expected. As it turned out, the contract, and that clause in particular, became a basis for a prolonged litigation. In 1990, the courts awarded Genentech over $150 million in a decision determining that Lilly had violated the 1978 contract by using a component of Genentech’s insulin technology in making its own human growth hormone product. [Page 95] Perkins believed that the 8 percent royalty rate was unusually high, at a time when royalties on pharmaceutical products were along the lines of 3 or 4 percent. “It was kind of exorbitant royalty, but we agreed anyway – Lilly was anxious to be first (with human insulin)” […]The big company – small company template that Genentech and Lilly promulgated in molecular biology would become a prominent organizational form in a coming biotechnology industry. [Page 97]
The invention of a new culture
Young as Swanson was, he kept everyone focused on product-oriented research. He continued to have scant tolerance for spending time, effort, and money on research not tied directly to producing marketable products. “We were interested in making something usable that you could turn into a drug, inject in humans, take to clinical trials.” A few year before his premature death, Swanson remarked, “I think one of the things I did best in those days was to keep us very focused on making a product.“ His goal-directed management style differed markedly from that of Genentech’s close competitors. [Page 129]
But at the same time Boyer would guarantee a high quality research level by encouraging employees to write the best possible scientific articles. This guaranteed the reputation of Genentech in the academic world.
A culture was taking shape at Genentech that had no exact counterpart in industry or academia. The high-tech firms in Silicon Valley and along Route 128 in Massachusetts shared its emphasis on innovation, fast-moving research, and intellectual property creation and protection. But the electronics and computer industries, and every other industrial sector for that matter, lacked the close, significant, and sustained ties with university research that Genentech drew upon from the start and that continue to define the biotechnology industry of today. Virtually every element in the company’s research endeavor – from its scientists to its intellectual and technological foundations – had originated in decade upon decade of accumulated basic-science knowledge generated in academic labs. […] At Boyer’s insistence, the scientists were encouraged to publish and engage in the wide community of science. [Page 131]
But academic values had to accommodate corporate realities: at Swanson’s insistence, research was to lead to strong patents, marketable products, and profit. Genentech’s culture was in short a hybrid of academic values brought in line with commercial objectives and practices. [Page 132]
Swanson was the supportive but insistent slave driver, urging on employees beyond their perceived limits: “Bob wanted everything. He would say, If you don’t have more things on your plate than you can accomplish, then you’re not trying hard enough. He wanted you to have a large enough list that you couldn’t possibly get everything done, and yet he wanted you to try.” […] Fledging start-ups pitted against pharmaceutical giants could compete mainly by being more innovative, aggressive, and fleet of foot. Early Genentech had those attributes in spades. Swanson expected – demanded – a lot of everyone. His attitude was as Roberto Crea recalled: “Go get it; be there first; we have to beat everybody else… We were small, undercapitalized, and relatively unknown to the world. We had to perform better than anybody else to gain legitimacy in the new industry. Once we did, we wanted to maintain leadership.” […] As Perkins said “Bob would never be accused of lacking a sense of urgency. “ […] Even Ullrich, despite European discomfort with raucous American behavior, admitted to being seduced by Genentech’s unswervingly committed, can-do culture. [Page 133]
New exit strategies
Initially Kleiner thought Genentech would be acquired by a major pharma company. It was just a question of when. He approached Johnson and Johnson and “floated the idea of a purchase price of $80 million. The offer fell flat. Fred Middleton [Genentech’s VP of finance], present at the negotiations, speculated that J&J didn’t have “a clue about what to do with this [recombinant DNA] technology – certainly didn’t know what it was worth. They couldn’t fit it in a Band-Aid mold”. J&J executives were unsure how to value Genentech, there being no standard for comparison or history of earnings.” [Page 140]
Perkins and Swanson made one more attempt to sell Genentech. Late in 1979, Perkins, Swanson, Kiley and Middleton boarded a plane for Indianapolis to meet with Eli Lilly’s CEO and others in top management. Perkins suggested a selling price of $100 million. Middleton’s view is that Lilly was hamstrung by a conservative “not invented here” mentality, an opinion supported by the drug firm’s reputation for relying primarily on internal research and only reluctantly on outside contracts. The company’s technology was too novel, too experimental, too unconventional for a conservative pharmaceutical industry to adopt whole-heartedly. [Page 141]
When Genentech successfully developed interferon, a new opportunity happened. Interferon had been discovered in 1957 and thought to prevent virus infection. In November 1978, Swanson signed a confidential letter of intent with Hoffmann – La Roche and a formal agreement in January 1980. They were also lucky: “Heyneker and a colleague attended a scientific meeting in which the speaker – to everyone’s astonishment given the field’s intense competitiveness – projected a slide of a partial sequence of fibroblast interferon. They telephoned the information to Goeddel, who instantly relay the sequence order to Crea. […] Crea started to construct the required probes. […] Goeddel constructed a “library” of thousands upon thousands of bacterial cells, seeking ones with interferon gene. Using the partial sequence Pestka retrieved, Goeddel cloned full-length DNA sequences for both fibroblast and leukocyte interferon. […] In June 1980, after filing patent protection, Genentech announced the production in collaboration with Roche.” [Page 145] Genentech could consider going public and after another fight between Perkins and Swanson, Genentech decided to do so. Perkins had seen that the year 1980 was perfect for financing biotech companies through a public offering but Swanson saw the challenges this would mean for a young company with nearly no revenue or product.
New role models
The 1980-81 period would see the creation of a fleet of entrepreneurial biology-based companies – Amgen, Chiron, Calgene, Molecular Genetics, Integrated Genetics, and firms of a lesser note – all inspired by Genentech’s example of a new organizational model for biological and pharmaceutical research. Before the IPO window closed in 1983, eleven biotech companies in addition to Genentech and Cetus, had gone public*. […] But not only institutions were transformed. Genentech’s IPO transformed Herb Boyer, the small-town guy of blue-collar origins, into molecular biology’s first industrial multimillionaire. For admiring scientists laboring at meager academic salaries in relative obscurity, he became a conspicuous inspiration for their own research might be reoriented and their reputation enhanced. If unassuming Herb – just a guy from Pittsburgh, as a colleague observed – could found a successful company with all the rewards and renown that entailed, why couldn’t they? [Page 161]
*: According to one source, the companies staging IPO were Genetic Systems, Ribi Immunochem, Genome Therapeutics, Centocor, Bio-Technology General, California Biotechnology, Immunex, Amgen, Biogen, Chiron, and Immunomedics. (Robbins-Roth, From Alchemy To Ipo: The Business Of Biotechnology)
Following these three posts, I might write a fourth one about academic licenses in the biotechnology if and when I find some time…
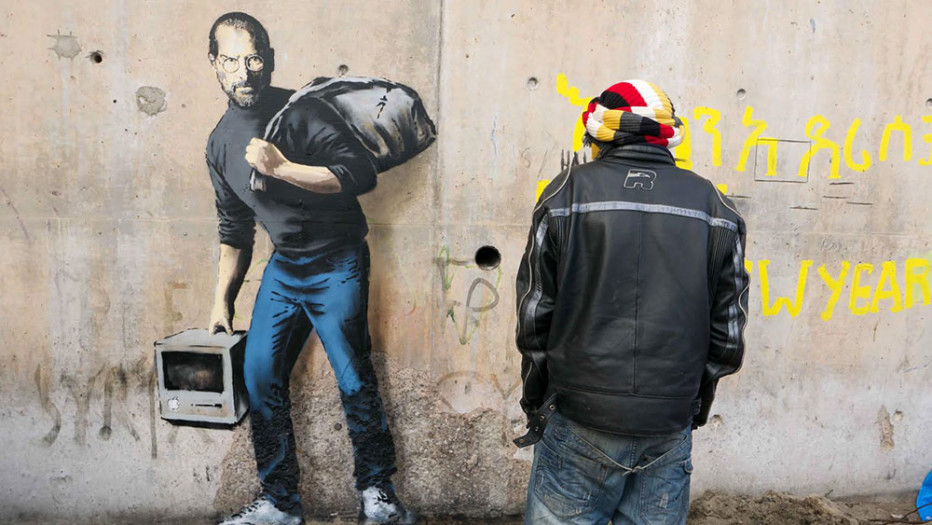
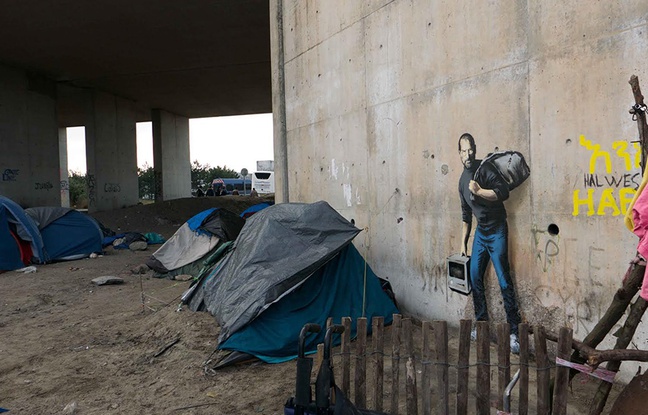
When Entrepreneurship Meets Street Art
From time to time, I post articles not related to start-ups and entrepreneurship, but to other topics such as Street Art for example. Now comes the opportunity to join both thanks to Banksy. Indeed I can even relate both to migrants (who are a critical component of entrepreneurship). Banksy recently created the following Street Art work:
Banksy explained: “We’re often led to believe migration is a drain on the country’s resources, but Steve Jobs was the son of a Syrian migrant. Apple is the world’s most profitable company, it pays over $7 billion a year in taxes—and it only exists because they allowed in a young man from Homs.” Do I need to add about the importance of migrants in high-tech entrepreneurship? If yes, just read again AnnaLee Saxenian, Migration, Silicon Valley, and Entrepreneurship.
The business of biotech – Part 2
After a short analysis of Amgen through the book by Gordon Binder – Science Lessons – here’s a more statistical description of the world of biotech. I am considering a third part about Genentech as a conclusion of this group. For several years, I have been manually building the capitalization tables of start-ups in general thanks to their IPO documents. They probably contain errors as the exercise requires attention and accuracy, but I imagine that these errors are averaged. I have today more than 350 cases, which are published on Slideshare.
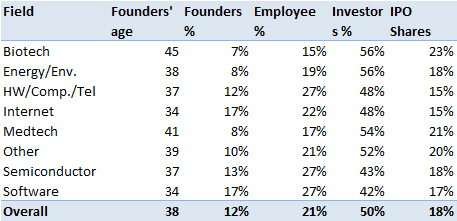
At the end of this document, I have added some synthetic data from which I extract the following. Remember that my sampling is done as I find new companies, so it is not totally random or statistically neutral …
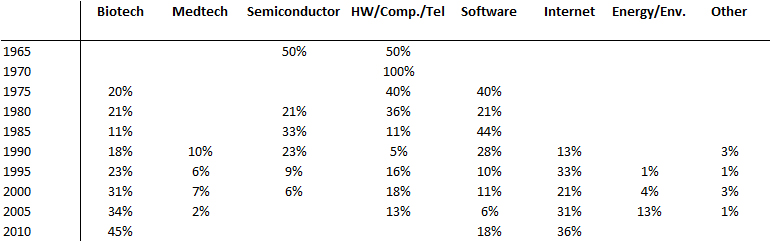
Biotechnology represents a significant part of my data, I will return to this later. VC fundraising is not more important than in other areas, which may seem surprising but it is because a biotech start-up goes public in term of maturity well before the start-ups of other fields. Besides their sales level ($11M on average) is much lower than the others ($114M for the average of all). Also they count 71 employees against 521 for the full set. The Amgen example illustrated that an IPO in fact more a complementary VC round than a market validation. However the first round is much bigger, probably because of the resources required for the initial proof of concept. The (profits and) losses are similar to other areas (excluding software and internet).
Now a small digression about the founders and the sharing of equity. They are much older (45 years) than average (38 years) and only come close the founders of medtech start-up. Probably because of the specific domain (length of academic curriculum and difficulties in inventing without a long experience). Another consequence of the dynamics of the field (including the uncertainties), the founders retain less equity at the IPO and investors get a larger share.
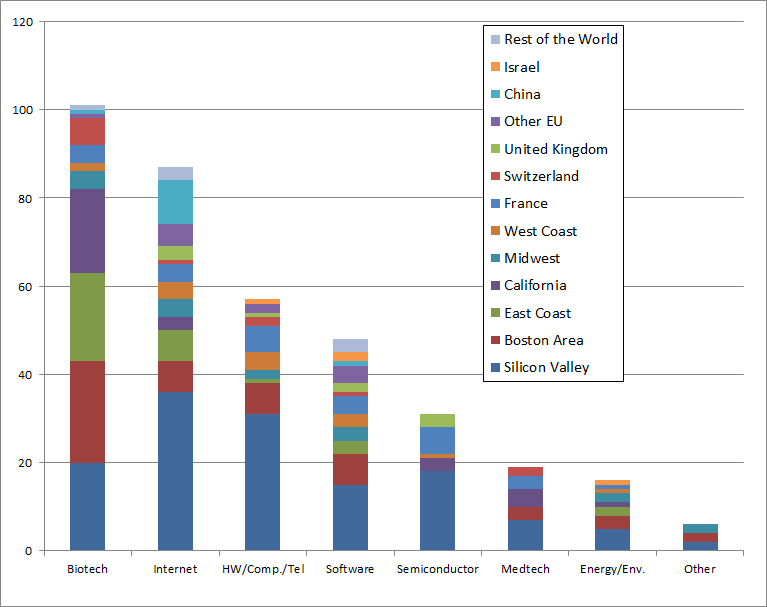
I now return to the biotech industry through its geography first and its timeline later. One known fact – the importance of the Boston area and the East Coast of the USA in general – and perhaps a surprise – the just as great importance of Silicon Valley and California more generally. It is often believed that the Boston area is the site of biotechnology, which is true with respect to other areas, but the West Coast is just as creative and entrepreneurial.
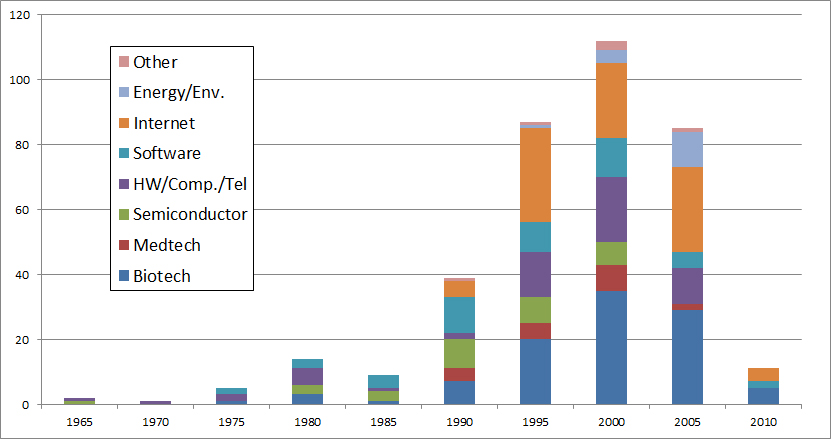
Finally it would be wrong to believe that the Internet has removed biotech. The periods here represent the years of creation of the startups. Biotech is the main field (over one third) since the 2000’s whereas they accounted for less than a quarter before. Again remember that my sample is not statistically validated …
Elon Musk and the Secret Sauce of Entrepreneurship (according to Tim Urban)
A student of mine (thanks 🙂 ) just sent me a link to amazingly great blog articles about Elon Musk. I had never of heard of the author, Tim Urban, and his blog Wait But Why but I will certainly follow his work from now on.
Tim Urban has written four articles about “the world’s most remarkable living entrepreneur.”
Part 1: Elon Musk: The World’s Raddest Man.
Part 2: How Tesla Will Change the World.
Part 3: How (and Why) SpaceX Will Colonize Mars.
Part 4: The Chef and the Cook: Musk’s Secret Sauce.
These 4 posts represent hundreds of pages if you print them. No kidding. I’ve read part 4 and it was a real (positive) shock. Tim Urban explains Musk’s entrepreneurial strengths. I just give some extracts but if must read it all (if you find the time).
“I think generally people’s thinking process is too bound by convention or analogy to prior experiences. It’s rare that people try to think of something on a first principles basis. They’ll say, “We’ll do that because it’s always been done that way.” Or they’ll not do it because “Well, nobody’s ever done that, so it must not be good.” But that’s just a ridiculous way to think. You have to build up the reasoning from the ground up —“from the first principles” is the phrase that’s used in physics. You look at the fundamentals and construct your reasoning from that, and then you see if you have a conclusion that works or doesn’t work, and it may or may not be different from what people have done in the past.” […] Musk is an impressive chef for sure, but what makes him such an extreme standout isn’t that he’s impressive — it’s that most of us aren’t chefs at all. […] “When I was a little kid, I was really scared of the dark. But then I came to understand, dark just means the absence of photons in the visible wavelength—400 to 700 nanometers. Then I thought, well it’s really silly to be afraid of a lack of photons. Then I wasn’t afraid of the dark anymore after that.” That’s just a kid chef assessing the actual facts of a situation and deciding that his fear was misplaced. As an adult, Musk said this: “Sometimes people fear starting a company too much. Really, what’s the worst that could go wrong? You’re not gonna starve to death, you’re not gonna die of exposure—what’s the worst that could go wrong?” Same quote, right? […] That’s Elon Musk’s secret sauce. Which is why the real story here isn’t Musk. It’s us. […] People believe thinking outside the box takes intelligence and creativity, but it’s mostly about independence. When you simply ignore the box and build your reasoning from scratch, whether you’re brilliant or not, you end up with a unique conclusion—one that may or may not fall within the box.
Then Tim Urban quotes Steve Jobs from his famous speech at Stanford in 2005 (I think): “When you grow up, you tend to get told the world is the way it is and your life is just to live your life inside the world. Try not to bash into the walls too much. Try to have a nice family life, have fun, save a little money. That’s a very limited life. Life can be much broader once you discover one simple fact. And that is: Everything around you that you call life was made up by people that were no smarter than you. And you can change it, you can influence it, you can build your own things that other people can use. Once you learn that, you’ll never be the same again.”

And all this reminds me about an essay I mentioned in the conclusion of my book, an essay by Wilhelm Reich, the great psychoanalyst, who he wrote in 1945: “Listen, Little Man”. A small essay by the number of pages, a big one in the impact it creates. “I want to tell you something, Little Man; you lost the meaning of what is best inside yourself. You strangled it. You kill it wherever you find it inside others, inside your children, inside your wife, inside your husband, inside your father and inside your mother. You are little and you want to remain little.” The Little Man, it’s you, it’s me. The Little Man is afraid, he only dreams of normality; it is inside all of us. We hide under the umbrella of authority and do not see our freedom anymore. Nothing comes without effort, without risk, without failure sometimes. “You look for happiness, but you prefer security, even at the cost of your spinal cord, even at the cost of your life”.
Tim Urban is absolutely right and you need to read his piece about dogma and tribes. He made me think again of my readings of the great French philosopher Cynthia Fleury and how we need to balance the individuals and the groups and why democracy is a fragile jewel of societies…
PS: I totally forgot to mention a video that a colleague of mine (thanks to her now 🙂 ) mentioned a few days ago. BY one of these nice coincidences of life, it is precisely one of the arguments of Tim Urban about why some people are “cooks” (followers or incremental innovators) and others “chefs” (disruptive innovators). Enjoy!
The business of biotechnology – Part 1 : Amgen
I do not know much about biotechnology (my background is IT). Though a start-up is a start-up, I always had the feeling that biotech was a different world. You often read that it easily takes ten years to develop a drug, so that biotech start-ups do not have any sales from products for even longer (with revenue coming only from R&D deals with big pharma). You also hear about going public through an IPO far before your product is on the market, something unusual in the IT world (except during the Internet bubble). Finally the financing needs from VCs seem to be much larger than in IT.
I have already written articles about this topic and you can find them under the tag biotech but I plan to write soon three new posts on the topic, related to recent readings and analysis:
– this post deals with my reading of Science Lessons – What the Business of Biotech Taught Me About Management by Gordon Binder, former CEO of Amgen & Philip Bashe.

– I will then give an update of cap. tables with 350+ companies. I will focus then on biotech firms.
– Finally, I should read soon another book, Genentech – the Beginnings of Biotech by Sally Smith Hughes. Hopefully it will be as good as Science Lessons. (And here is my synthesis, Part 3: Genentech.)
The Business of Biotech
Amgen is probably the biggest biotech firm today (with a market cap. around $100B in 2015). “The company debuted on Nasdaq stock exchange on June 17, 1983. Considering that Amgen didn’t have any products at the time, going public seemed premature to some observers. And it was; an IPO wasn’t in the original timetable at all. But our other sources of capital had shriveled up like foliage during Southern California’s dry season, leaving an initial public offering our only option.” [Page 6]
Amgen’s secret weapon
From the beginning, Amgen was a magnet for gifted, innovative men and women. How does an organization attract outstanding employees? […] Certainly we offered attractive salaries and benefits, and the stock options made available to every Amgen employee no doubt induced some folks to stay who otherwise might have sought opportunities elsewhere. As numerous studies have established, however, pay and perks aren’t what foster long-term employee loyalty. It’s something more profound, something that speaks to the very soul of a company. […] Because a company’s culture emerges from its values, we interviewed hundreds of staff members in all areas of Amgen to learn which values they believed constituted the core of that culture. Today it seems that every company under the sun (or under a cloud) has a values statement. Some are written by the CEO, and others are concocted by the public relations or human resource department. Sometimes they’re written by consultants who don’t even work there. More often than not, the statement doesn’t truly reflect the organizations values; it’s either a wish list of what the company aspires to be or a PR tool for impressing customers, suppliers, and investors. [Page 9]
As Amgen grew exponentially, we constantly wrestled with the same quandary that confronts most flourishing companies at some point: how to remain nimble when you’re no longer a small start-up. You do it by decentralizing power, of course, but also by establishing an entrepreneurial culture that embraces change and encourages innovation. For that to happen, management must empower its people and then support them 100 percent, because staffers do not offer ideas freely if they secretly believe they will be hung out to dry should their promising project flop. In an industry such as biotechnology, failures abound. Had Amgen not lived its principle “Employees must have the freedom to make mistakes,” we would not have survived. [Page 14]
Amgen’s financings
Amgen was incorporated on April 8, 1980. Then Bowes the cofounder and 1st investor “coaxed six venture-capitalist into putting up roughly $81,000 apiece in seed money.” [Page 18] George Rathmann became the CEO and only employee in the company. When the company needed a serious series A funding, Rathmann was convinced it needed much more than the typical $1M first round and looked for $15M. No VC would have agreed, so he convinced first corporations. Abbott invested $5M (which would be worth $700M in 1990). Tosco added $3.5M. And New Court (managed by Rothschild) would then invest $3M. The Series closed with $19.4M on January 23, 1981. Then the IPO brought $42M in 1983, but this was only another beginning as more public financings would follow: $35M in 1986 for the “secondary” and $120M for a third financing the next year.
Here is the cap. table of Amgen at IPO:
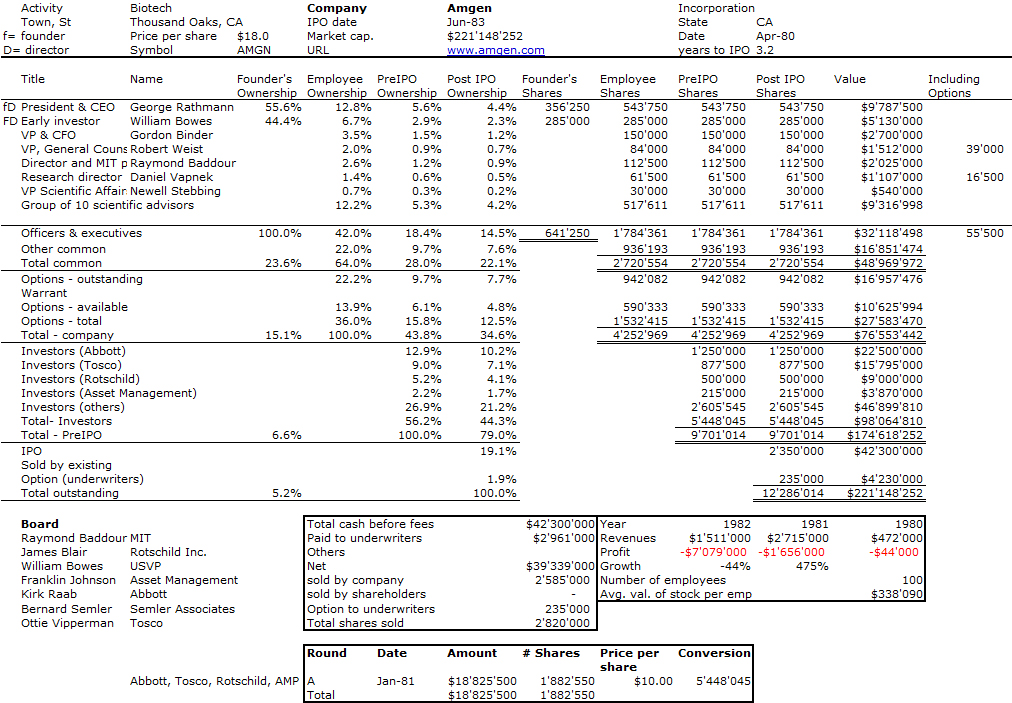
Though biotech start-ups have longer horizons that IT firms, the intensity of activities is very similar. Binder shows examples such as Amgen’s IPO (chapter 2), the discovery of EPO (chapter 4) and its FDA approval (chapter 5). There is however a major difference. Biotech is about science and research. “It’s fair to say that at many companies, if not most, sales and marketing dominate corporate strategizing; the scientific or creative end may be behind the wheel, but ultimately the sales-and-marketing people commandeer the road map, barking out directions from the passenger seat. Not so in the field of biotechnology and certainly not at Amgen where even the company’s location was chosen to attract first rate scientists. Our headquarters sat more or less equidistant to the three principal research centers in southern California: the University of California at Los Angeles (UCLA), the University of California at Santa Barbara (UCSB), and the California Institute of Technology (CalTech), in Pasadena”. [Pages 57-58]
Amgen’s partners
“Success is the ability to survive your mistakes.” George Rathman
Chapter 6 (Partnerships Made in Heaven – and That Other Place) is a must read. Binder explains how critical good and bad partners may be and again this is linked to values and ethics. Binder claims that managers are much more careful when they hire someone than when they sign a partnership.
“Our search for a corporate partner started at home. Much to our shock, not a single U.S. pharmaceutical firm showed interest. […] Abbott Laboratories, one of Amgen’s original investors, had the opportunity to be involved in the Epogen project. CEO and Chairman Bob Schoellhorn turned it down. He’d been influenced by Abbott’s chief chemist, who apparently didn’t think much of drugs based on large proteins. As we would discover, that bias was not unique to Abbott; in fact it dominated traditional pharma. One company’s representative informed us that his bosses were passing on Epogen because the opportunity was too small; their market research department predicted sales would never eclipse $50 million per year (For the record, the drug generates $10 billion in annual revenue. Some market research!).” [Page 126]
Their first partner would be Kirin, the Japanese beer company with which trust, transparency and little paper work helped in building a great partnership. This was not the case with Johnson & Johnson. “To this day, contempt for Amgen’s former partner runs so deep that many employees proudly proclaim their homes to be 100 percent “J&J free.” Considering that Johnson & Johnson and its many businesses sell more than one thousand products, from Band-Aids to Tylenol, that’s no small feat.” [Page 133]
Amgen also has academic partners: “Memorial Sloan-Kettering possessed a mixture of about two hundred proteins. But it didn’t have the technology to separate them. Amgen did. […Amgen] discovered the human gene that produces G-CSF, located on chromosome 17. Once isolated, the gene was cloned using the same process as for human EPO. Memorial Sloan-Kettering had filed a weak patent, not knowing what it actually had. Therefore, said my general counsel, Amgen was legally free to process on its own, without paying a royalty to MSKCC. That didn’t seem ethical to me; without Sloan-Kettering, we wouldn’t have stumbled across filgrastim (Neupogen’s generic name). We negotiated a license with a modest royalty.” [Pages 143-44]
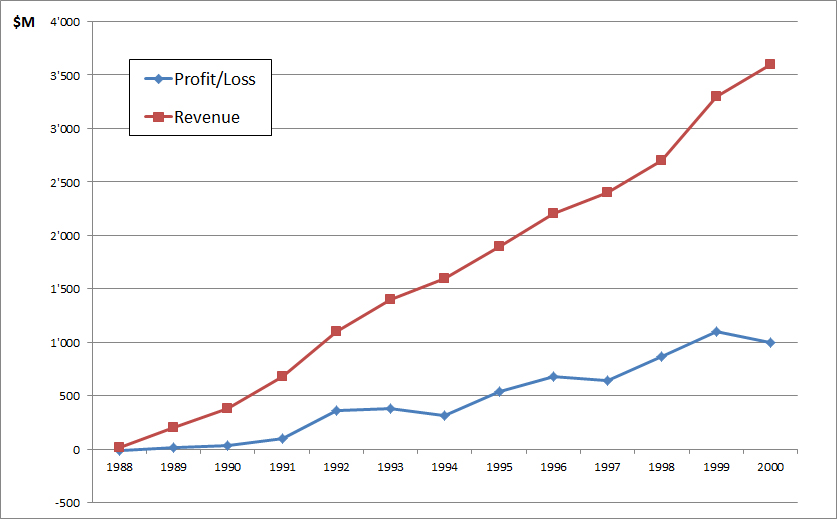
Finally for now, here is Amgen growth curve – revenues & profits. When a biotech start-up is successful, the numbers are impressive…