Since I have been interested in start-ups, i.e. 1997, I have always been puzzled about the macroeconomic impact of start-ups, i.e. fast growing companies, mostly in high-tech. The famous Intel, Apple, Microsoft, Cisco, Yahoo, and other Google have an impact, but what is it exactly for the economy?
Surprisingly, it is not that well-known. I have read in the past weeks some recent papers on the topic that you may download if you are interested. The Kauffman foundation which I have mentioned already is doing a great job and particularly Dane Strangler. He is the author of High-Growth Firms and the Future of the American Economy and of Exploring Firm Formation: Why is the Number of New Firms Constant? as well as Where Will The Jobs Come From?
Thanks to his reports, I became aware of older studies such as Gazelles as Job Creators – A Survey and Interpretation of the Evidence and High-Impact Firms: Gazelles Revisited both dated 2008. Finally the Brittish government has its own study, High growth firms in the UK: Lessons from an analysis of comparative UK performance. This last report is interesting as it not only considers gazelles, the fast growing companies, but also gorillas, the young fast growing companies which reached a large size in less than 10 or 15 years.
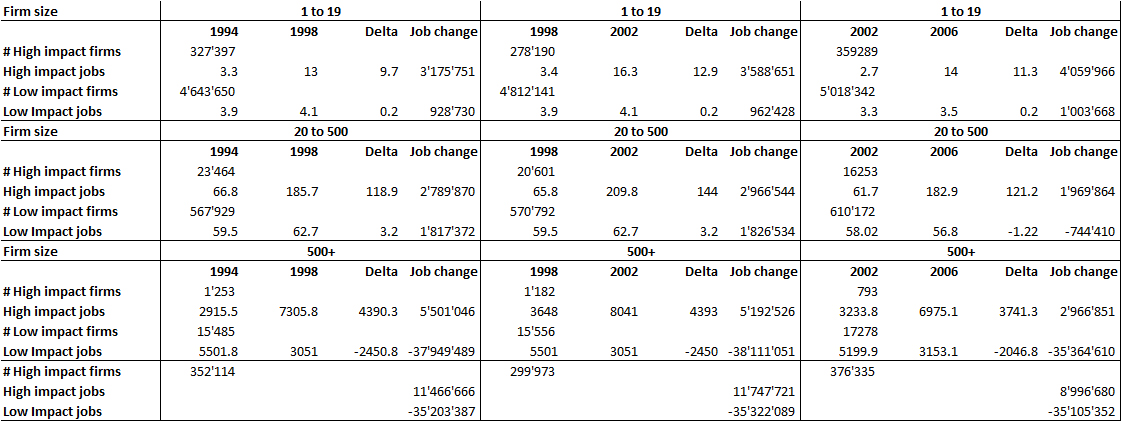
The first answers were provided in 1981 by David Birch who showed that large firms were not the providers of job creation anymore. But even today, the answer to the question is not so clear. At least it took me longer than I would have thought to understand what all these reports claimed. So for example, here is a table of how small, mid-size and large firms create jobs in the USA. The numbers come with no real guaranty as I have compiled them from a number of sources, mostly the High-Impact Firms: Gazelles Revisited
So what does this mean? First high-impact firms contribute to most of the new job creation in the USA. What are high-impact firms? These are the firms which grow at a 20% annual rate (in jobs and sales*), the fast growing firms. As you may see, low-impact firms also create jobs but only if they are SMEs (small and mid-size). It explains why we think that fast-growing small firms are so important.
But it is an over-simplification. High-impact firms are not small and all these studies also show that:
– they are not young. On average, they are 25-years old.
– they are not necessarily high-tech, they can be found in all sectors of the economy.
– a minority is VC-backed. This is obvious as we have here about 300’000 gazelles and probably only a few thousand companies are VC-backed each year in the US.
More on gazelles here. Now, what about Gorillas? Gorillas are extremely fast growing and young companies. The UK report above defines them as less than 15 years old, with the same growth as gazelles. I remember that Geoffrey Moore defines them as leaders in their market. Well, not much is known about them. The UK report mentions there was no Gorilla in the UK whereas Yahoo, eBay, Amazon, Yahoo and Google were Gorillas in the USA.
Dane Strangler in his report is providing more interesting data. They are not the gorillas per se, but probably quite close:
– In any given year, the top-performing 1 percent of young firms generate roughly 40 percent of new job creation.
– Fast-growing young firms, comprising less than 1 percent of all companies, generate roughly 10 percent of new jobs in any given year.
Qiote impressive! Well, I still do not have all the answers I would like to have, but I now know gazelles are important, and gorillas maybe even more. And at the end, what is the impact of high-tech, of venture capital is just another but interesting story!
*: Growth in terms of jobs is more complex than 20%… experts use the Employment Growth Quantifier (EGQ), that is the product of the absolute and percent change in employment over a four-year period of time and take it as bigger than 2 for “high-impact”… A 20% increase in sales is also a factor 2 over the same period of time.